|
|
'자바스크립트'에 해당되는 글 15건
- 2010.05.11 XML Parser javascript class v1.0.0
- 2008.02.20 JavaScript 강좌 references. 2
- 2008.02.20 JavaScript Tips
- 2008.02.20 JavaScript Event
- 2008.02.20 JavaScript DOM
- 2008.02.20 javascript object, class & inheritance, sigletons
- 2008.02.20 내장객체, BOM, DOM, 사용자 정의 객체
- 2008.02.20 objects, collections, linkage, invocations, this, typeof, closure, namespace, inheritance
- 2008.02.20 try-catch-throw, special text
- 2008.02.20 JavaScript Loops
ITWeb/개발일반 2010. 5. 11. 12:34
XMLHttpRequest 와 더불어 유용할 것 같아서 만들었습니다.
역시 다른데 코드는 제 스타일도 아니고 읽기도 힘들고 그래서.. 후다닥 만들었다는..
recursive call 을 하기는 하지만 나름 쉽게 작성했습니다.
코드 가지고 태클은 금지.. ㅎㅎ
/*
* XMLParser Control Module
*
* @package
* @path
* @filename xmlparser.js
* @author
* @date 2010/05/03
*
* Change History
* Date Engineer Type Description
* ---------- ------------------ --------- --------------------
* 2010/05/03 Henry Jeong create initialize
*/
/*
*
* XMLParser module object
*
*/
var JXmlParser = function() {
};
/*
*
* xml parser variables
*/
JXmlParser.prototype.vars = {
parser : null,
doc : null,
xmldata : null,
root : null,
xml : null
}
JXmlParser.prototype.init = function() {
if (window.DOMParser) {
JXmlParser.vars.parser = new DOMParser();
JXmlParser.vars.doc = JXmlParser.vars.parser.parseFromString(
JXmlParser.vars.xmldata, "text/xml");
JXmlParser.vars.root = JXmlParser.vars.doc.childNodes.item(0);
} else {
JXmlParser.vars.doc = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLDOM");
JXmlParser.vars.doc.async = "false";
JXmlParser.vars.doc.loadXML(JXmlParser.vars.xmldata);
JXmlParser.vars.root = JXmlParser.vars.doc.documentElement;
}
JXmlParser.vars.xml = new Object();
JXmlParser.vars.xml["length"] = JXmlParser.vars.root.childNodes.length;
}
JXmlParser.prototype.setXml2Array = function(pobj, node) {
var len = node.length;
if (window.DOMParser) {
for ( var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (node[i].nodeName.charAt(0) == "#") {
continue;
}
pobj[i] = new Object();
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName] = new Object();
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["value"] = node[i].textContent;
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["length"] = node[i].childNodes.length;
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["attributes"] = new Object();
if (node[i].attributes && node[i].attributes.length > 0) {
var loop = node[i].attributes.length;
for ( var j = 0; j < loop; j++) {
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["attributes"][node[i].attributes[j].nodeName] = node[i].attributes[j].nodeValue;
}
}
if (node[i].childNodes.length > 0) {
JXmlParser.setXml2Array(pobj[i][node[i].nodeName],
node[i].childNodes, node[i].childNodes.length);
}
}
} else {
for ( var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (node[i].nodeName.charAt(0) == "#") {
continue;
}
pobj[i] = new Object();
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName] = new Object();
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["value"] = node[i].text;
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["length"] = node[i].childNodes.length;
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["attributes"] = new Object();
if (node[i].attributes && node[i].attributes.length > 0) {
var loop = node[i].attributes.length;
for ( var j = 0; j < loop; j++) {
pobj[i][node[i].nodeName]["attributes"][node[i].attributes[j].nodeName] = node[i].attributes[j].text;
}
}
if (node[i].childNodes.length > 0) {
JXmlParser.setXml2Array(pobj[i][node[i].nodeName],
node[i].childNodes, node[i].childNodes.length);
}
}
}
}
JXmlParser = new JXmlParser();
/*
* <script type="text/javascript"> <!-- var objDivDebug =
* document.getElementById("divDebug");
*
function run() {
JXmlParser.vars.xmldata = "<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?><parser><totalcount type='number'><total>A</total><total>B</total></totalcount><items name='user' type='image'><item><seq>1</seq><id><![CDATA[jjeong****]]></id><originalImage><![CDATA[http://www.naver.com]]></originalImage><viewImage><![CDATA[http://www.naver.com]]></viewImage><thumbImage><![CDATA[http://www.naver.com]]></thumbImage><cheerMessage><![CDATA[한국어 테스트.]]></cheerMessage><register><![CDATA[20100503175621]]></register></item><item><seq>2</seq><id><![CDATA[layd****]]></id><originalImage><![CDATA[http://www.naver.com]]></originalImage><viewImage><![CDATA[http://www.naver.com]]></viewImage><thumbImage><![CDATA[http://www.naver.com]]></thumbImage><cheerMessage><![CDATA[CHEER MESSAGE]]></cheerMessage><register><![CDATA[20100503175621]]></register></item></items></parser>";
JXmlParser.init();
JXmlParser.setXml2Array(JXmlParser.vars.xml, JXmlParser.vars.root.childNodes);
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml.length + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[0]["totalcount"].value + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[0]["totalcount"].attributes.type + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[0]["totalcount"].length + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[0]["totalcount"][0]["total"].value + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[0]["totalcount"][0]["total"].length + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[0]["totalcount"][1]["total"].value + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[0]["totalcount"][1]["total"].length + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[1]["items"].value + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[1]["items"].attributes.name + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[1]["items"].length + "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[1]["items"][0]["item"] .length+ "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[1]["items"][0]["item"][0]["seq"] .value+ "<br>";
objDivDebug.innerHTML += JXmlParser.vars.xml[1]["items"][0]["item"][1]["id"] .value+ "<br>";
}
* //--> </script>
*/
*/
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 17:52
•
– yahoo.com YUI JavaScript ENG
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 17:48
•Semicolon insertion
–-When the compiler sees an error, it attempts to replace a nearby linefeed with a semicolon and try again.
–-This should alarm you.
–-It can mask errors.
–-Always use the full, correct forms, including semicolons.
•Comma
–-Good: [1, 2, 3]
–-Bad: [1, 2, 3,]
•Required block
–-Good:
§if (a) {
§ b();
§}
–-Bad:
§if (a) b();
•== and !=
–-Bad
§if (a == null) { ... }
–-Good:
§if (a === null) { ... }
§if (!a) { ... }
•Common subexpression removal
•Loop invariant removal
for (var i = 0; i < divs.length; i += 1) {
divs[i].style.color = "black";
divs[i].style.border = thickness + 'px solid blue';
divs[i].style.backgroundColor = "white";
} ----->
var border = thickness + 'px solid blue',
nrDivs = divs.length;
for (var i = 0; i < nrDivs; i += 1) {
var ds = divs[i].style;
ds.color = "black";
ds.border = border;
ds.backgroundColor = "white";
}
•Strings
–-Concatenation with +
§Each operation allocates memory
–foo = a + b;
–-Concatenate with array.join('')
§The contents of an array are concatenated into a single string
–-Comparison
§a) foo = a + b; vs b) foo = [a, b].join('');
–a) < b)
§a) foo = 'a' + 'b'; vs b) foo = ['a', 'b'].join('');
–a) > b)
•-Place <script src> tags as close to the bottom of the body as possible. (Also, place CSS <link> as high in the head as possible.)
•-Minify and gzip script files.
•-Reduce the number of script files as much as possible.
•<script></script>
–<!-- // -->
§Hack for Mosaic and Navigator 1.0.
–language=javascript
§Deprecated.
–src=URL
§Highly recommended.
§Don't put code on pages.
–type=text/javascript
§Ignored.
•document.write
–-Allows JavaScript to produce HTML text.
–-Before onload: Inserts HTML text into the document.
–-After onload: Uses HTML text to replace the current document.
–-Not recommended.
•name
–-Identifies values in form data
–-Identifies a window/frame
•id
–-Uniquely identifies an element
•document.all
–-Microsoft feature, rejected by W3C and most other browsers.
–-It acts as a function or array for accessing elements by position, name, or id.
–-Avoid it.
•Manipulating elements
–-Old
§if (my_image.complete) {
§ my_image.src = superurl;
§}
–-New
§if (my_image.getAttribute('complete')) {
§ my_image.setAttribute('src', superurl);
§}
•Element id 를 통한 접근
–var oElement = null;
–if ( document.getElementById ) {
– oElement = document.getElementById(ID);
–} else if ( document.layers ) {
– oElement = document.layers[ID];
–} else if ( document.all ) {
– oElement = document.all[ID];
–}
•JavaScript XMLHttpRequest
•DOM3 Events, Core
•2006
var oHttp = false;
var aMsxmlType = [
'MSXML2.XMLHTTP.5.0',
'MSXML2.XMLHTTP.4.0',
'MSXML2.XMLHTTP.3.0',
'MSXML2.XMLHTTP',
'Microsoft.XMLHTTP'
];
if ( window.XMLHttpRequest ) {
try {
oHttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
} catch(e) {
oHttp = false;
}
} else if ( window.ActiveXObject ) {
for ( i=0; i<this.aMsxmlType.length; i++ ) {
try {
oHttp = new ActiveXObject(this.aMsxmlType[i]);
if ( oHttp ) {
break;
}
} catch(e) {
oHttp = false;
}
}
}
•JavaScritp XMLDOM
–var oXmlDoc = null;
–if ( window.ActiveXObject ) {
– oXmlDoc = new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLDOM");
–} else if ( document.implementation && document.implementation.createDocument ) {
– oXmlDoc = document.implementation.createDocument("", "", null);
–}
–IE/FF (xml file)
§Using XMLDOMObject. getElementsByTagName(..)
–FF (xml string)
§var oDomParser=new DOMParser();
§var oDoc = oDomParser.parseFromString(XMLSTRING,"text/xml");
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 17:41
•-The browser has an event-driven, single-threaded, asynchronous programming model.
•-Events are targeted to particular nodes.
•-Events cause the invocation of event handler functions.
•-Events are normally used in combination with functions, and the function will not be executed before the event occurs!
|
Attribute |
The event occurs when... |
FF |
N |
IE |
|
onabort |
Loading of an image is interrupted |
1 |
3 |
4 |
|
onblur |
An element loses focus |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
onchange |
The user changes the content of a field |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
onclick |
Mouse clicks an object |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
ondblclick |
Mouse double-clicks an object |
1 |
4 |
4 |
|
onerror |
An error occurs when loading a document or an image |
1 |
3 |
4 |
|
Onfocus |
An element gets focus |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
onkeydown |
A keyboard key is pressed |
1 |
4 |
3 |
|
onkeypress |
A keyboard key is pressed or held down |
1 |
4 |
3 |
|
onkeyup |
A keyboard key is released |
1 |
4 |
3 |
|
onload |
A page or an image is finished loading |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
onmousedown |
A mouse button is pressed |
1 |
4 |
4 |
|
onmousemove |
The mouse is moved |
1 |
6 |
3 |
|
onmouseout |
The mouse is moved off an element |
1 |
4 |
4 |
|
onmouseover |
The mouse is moved over an element |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
onmouseup |
A mouse button is released |
1 |
4 |
4 |
|
onreset |
The reset button is clicked |
1 |
3 |
4 |
|
onresize |
A window or frame is resized |
1 |
4 |
4 |
|
onselect |
Text is selected |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
onsubmit |
The submit button is clicked |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
onunload |
The user exits the page |
1 |
2 |
3 |
•Event parameter
–-function getCBEvent (oNsEvent, PARAM1…) {
– // window.event : ff 에서 undefined
– var oEvent = oNsEvent || window.event;
– var oTarget = oEvent.target || oEvent.srcElement;
–}
–onclick=“getCBEvent(event, param1,..,parmaN);”
–-Microsoft does not send an event parameter, use the global event object instead
•
Event listener.
–Classic
§node["on" + type] = f;
–Microsoft
§node.attachEvent("on" + type, f);
–W3C
§node.addEventListener(type, f, false);
–Example :
§if ( DOMObject.addEventListener ) {
§ DOMObject.addEventListener("click", getMsg, false);
§} else if (DOMObject.attachEvent ) {
§ DOMObject.attachEvent("onclick", getMsg);
§} else if (DOMObject.onclick ) {
§ DOMObject.onclick = getMsg; // or
§ DOMObject["onclick“] = getMsg;
§}
•Event bubbling
–-Event bubbling is that the event is delivered in elements, and so on until the event is canceled.
•Cancel bubbling
–-function cancelBubbling ( oEvent ) {
– if ( oEvent.stopPropagation ) {
– oEvent.stopPropagation(); // FF
– } else {
– oEvent.cacnelBubble = true; // IE
– }
–}
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 17:34
•Node
–-Retrieving nodes
§document.getElementById(id)
§document.getElementsByName(name)
§node.getElementsByTagName(tagName)
•Node
–Document tree structure
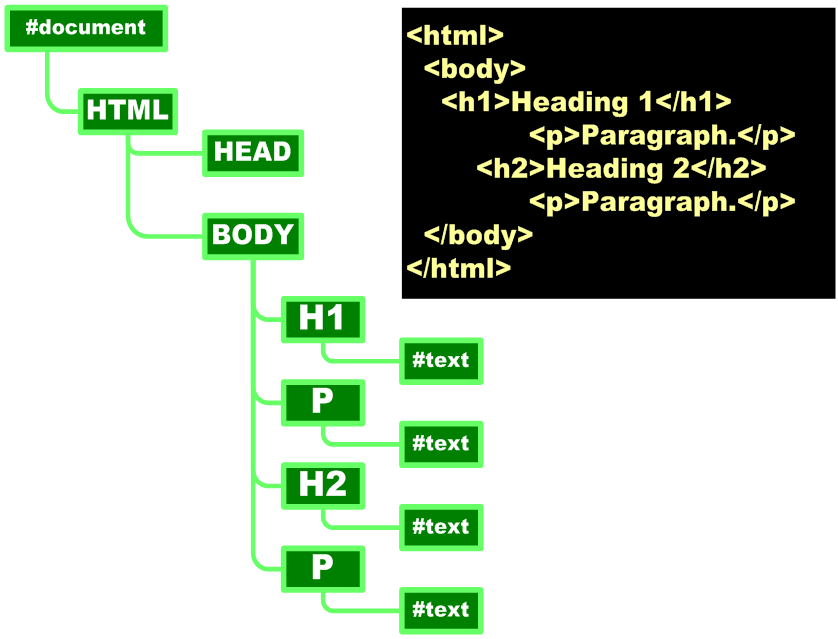
•Node
–-child, sibling, parent 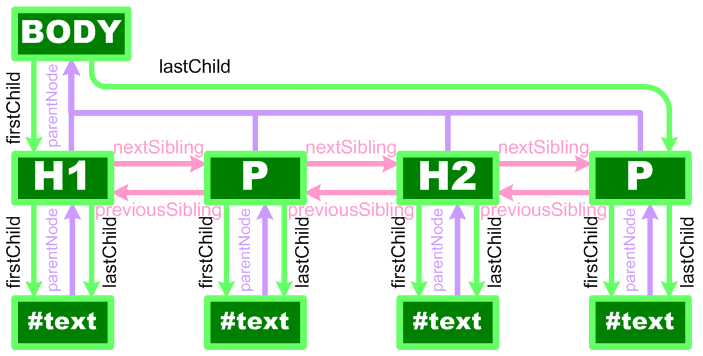
•Walk the DOM
–-Using recursion, follow the firstChild node, and then the nextSibling nodes.
§function walkTheDOM(node, func) {
§ func(node);
§ node = node.firstChild;
§ while (node) {
§ walkTheDOM(node, func);
§ node = node.nextSibling;
§ }
§}
•Style
–-node.className
–-node.style.stylename
–-node.currentStyle.stylename Only IE
–-document.defaultView(). getComputedStyle(node, ""). getPropertyValue(stylename);
§var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
§var nHeight = document.defaultView.getComputedStyle(oDiv, null).getPropertyValue("height");
Style names
CSS
•background-color
•border-radius
•font-size
•list-style-type
•word-spacing
•z-index
JavaScript
•backgroundColor
•borderRadius
•fontSize
•listStyleType
•wordSpacing
•zIndex
•Making elements
–-document.createElement(tagName)
§var hr = document.createElement("hr");
§document.body.appendChild(hr);
–-document.createTextNode(text)
§var txt = document.createTextNode("Hello!");
§document.body.appendChild(txt);
–-node.cloneNode(deep);
§cloneNode(true) clones the whole subtree rooted at the node
§cloneNode(false) only the node itself (and any attributes if it is an element) is cloned
–curr_node = root.firstChild;
–var new_node = curr_node.cloneNode(true);
–root.appendChild(new_node);
•Linking elements
–-node.appendChild(new)
–-node.insertBefore(new, sibling)
–-node.replaceChild(new, old)
–-old.parentNode.replaceChild(new, old)
•Removing elements
–-node.removeChild(old)
–-old.parentNode.removeChild(old)
•innerHTML
–-The W3C standard does not provide access to the HTML parser.
–-All A browsers implement Microsoft's innerHTML property.
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 17:08
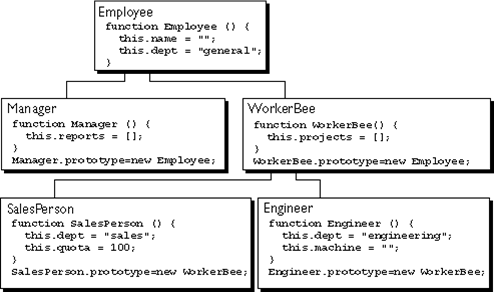
•Class & Inheritance
–-Prototypal Inheritance
|
var oldObject = {
firstMethod: function () { alert("first"); },
secondMethod: function () { alert("second"); }
};
var newObject = new Object(oldObject);
newObject.thirdMethod = function () { alert("third"); };
var myDoppelganger = new Object(newObject);
myDoppelganger.firstMethod(); // or
myDoppelganer[“firstMethod”](); |
var obj1 = function () {
this.title = "obj1";
}
var obj2 = function () {}
obj2.prototype = new obj1;
var obj2Class = new obj2();
alert(obj2Class.title);
obj1 = {
title:"obj1_"
}
obj2 = new Object(obj1);
alert(obj2.title); |
–-Method apply (Member variable)
§Function.apply(thisArg[, argArray])
–function Car(make, model, year) {
– this.make = make;
– this.model = model;
– this.year = year;
–}
–
–function RentalCar(carNo, make, model, year) {
– this.carNo = carNo;
– Car.apply(this, new Array(make, model, year));
–}
–
–myCar = new RentalCar(2134,"Ford","Mustang",1998);
–document.write("Your car is a " + myCar.year + " " + myCar.make + " " + myCar.model + ".");
–-Method apply (Member function)
§function TopClass (name, value) {
§ this.name = name;
§ this.value = value;
§ this.getAlertData = function () {
§ alert(this.name);
§ alert(this.value);
§ }
§}
§function SubClass (name, value, dept) {
§ this.dept = dept;
§ TopClass.apply(this, arguments);
§ this.getView = function () {
§ this.getAlertData();
§ }
§}
§//SubClass.prototype = new TopClass();
§var objSubClass = new SubClass("상위클래스","super","community");
§objSubClass.getView();
–-Method call
§Function.call(thisArg[, arg1[, arg2[, ...]]])
–function car(make, model, year) {
– this.make = make, this.model = model, this.year = year;
–}
–
–function hireCar(carNo, make, model, year) {
– this.carNo = carNo, car.call(this, make, model, year);
–}
•-Prototype
–Profiler = function () {..}
–Profiler.prototype.name = function () {..}
•-Namespace
–YAHOO = {};
•-new operator
–function object(o) {
– function F() {};
– F.prototype = o;
– return new F();
–}
–classA = new Profiler(); or classA = object(Profiler);
-Encapsulate (Parasitic)
|
YAHOO = {};
YAHOO.Trivia = function () {
var privateVar = "showPoser";
function privateNextPoser() {
alert("getNextPoser");
}
return {
getNextPoser: function (cat, diff) {
privateNextPoser();
},
showPoser: function () {
alert(privateVar);
}
};
} ();
function getFunc() {
var oObj = YAHOO.Trivia;
oObj.getNextPoser();
} |
YAHOO = {};
YAHOO.Trivia = function () {
var privateVar = "showPoser";
function privateNextPoser() {
alert("getNextPoser");
}
return {
getNextPoser: function (cat, diff) {
privateNextPoser();
},
showPoser: function () {
alert(privateVar);
}
};
};
function getFunc() {
var oObj = new YAHOO.Trivia();
oObj.getNextPoser();
} |
-Singletons
var singleton = function () {
var privateVariable;
function privateFunction(x) {
...privateVariable...
}
return {
firstMethod: function (a, b) {
...privateVariable...
},
secondMethod: function (c) {
...privateFunction()...
}
};
}();
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 16:47
•자바스크립트 내장 객체
–-Number
–-String
–-Date
–-Array
–-Boolean
–-Math
–-RegExp
•브라우저 객체 모델(BOM) 객체
-window
§document
–forms
–cookie
–links/anchors
–images
§navigator
§location
§frames
§screen
§history
The Document Object Model (DOM) is an API for HTML and XML documents.
-Core DOM
§defines a standard set of objects for any structured document
-XML DOM
§defines a standard set of objects for XML documents
-HTML DOM
§defines a standard set of objects for HTML documents
•DOM 객체
–DOM Level 1,2,3
§DOM1 : 1997~1998
§DOM2 : 2000~2003
§DOM3 : 2004
|
Specification |
|
|
|
DOM Level 1 |
|
DOM Level 1 (SE) |
|
|
|
DOM Level 2 Core |
|
DOM Level 2 HTML |
|
DOM Level 2 Views |
|
DOM Level 2 Style |
|
DOM Level 2 Events |
|
DOM Level 2 Traversal-Range |
|
|
|
DOM Level 3 Requirements |
|
DOM Level 3 Core |
|
DOM Level 3 Events |
|
DOM Level 3 Load and Save |
|
DOM Level 3 Validation |
|
DOM Level 3 XPath |
|
DOM Level 3 Views |
•개발자가 만든 사용자 정의 객체
–-JavaScript objects 와 prototype.
§YAHOO.util.Connect = {
– _msxml_progid:[],
– _http_headers:{},
– _has_http_headers:false,
– setProgId:function(){…}
–}
§Profiler = function () {
– var getProfilers; // private
– this.getProfiler = function () {…} // public
–}
§String.prototype.trim = functoin () {…}
§Profiler = new Object();
–Profiler.title = “YAHOO”;
–Profiler.author = “Jerry”;
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 16:36
Objects
–-Everything else is objects
–-Objects can contain data and methods
–-Objects can inherit from other objects.
•Collections
–-An object is an unordered collection of name/value pairs
–-Names are strings
–-Values are any type, including other objects
–-Good for representing records and trees
–-Every object is a little database
§var FUNC = function () {
§ var objDiv = document.createElement("div");
§ this.getCollection = function ( collection ) {
§ for ( i in collection ) {
§ objDiv.innerHTML += "name : " + i + "<br>value : " + collection[i] + "<br>";
§ }
§ document.body.appendChild(objDiv);
§ }
§}
§FUNC = new FUNC();
•Object Literals
–-Object literals are wrapped in { }
–-Names can be names or strings
–-Values can be expressions
–-: separates names and values
–-, separates pairs
–-Object literals can be used anywhere a value can appear
•Linkage
–-Objects can be created with a secret link to another object.
–-If an attempt to access a name fails, the secret linked object will be used.
–-The secret link is not used when storing. New members are only added to the primary object.
–-The object(o) function makes a new empty object with a link to object o.
function object(o) {
function F() {};
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
•JavaScript Invocations
–-If a function is called with too many arguments, the extra arguments are ignored.
–-If a function is called with too few arguments, the missing values will be undefined.
–-There is no implicit type checking on the arguments.
–-There are four ways to call a function:
§Function form
–functionObject(arguments)
§Method form
–thisObject.methodName(arguments)
–thisObject["methodName"](arguments)
§Constructor form
–new functionObject(arguments)
§Apply form
–functionObject.apply(thisObject, [arguments])
•JavaScript this
–-this is an extra parameter. Its value depends on the calling form.
–-this gives methods access to their objects.
–-this is bound at invocation time.
|
Invocation form |
this |
|
function |
the global object |
|
method |
the object |
|
constructor |
the new object |
JavaScript typeof
|
type |
typeof |
|
object |
'object' |
|
function |
'function' |
|
array |
'object' |
|
number |
'number' |
|
string |
'string' |
|
boolean |
'boolean' |
|
null |
'object' |
|
undefined |
'undefined' |
•Closure
–-The scope that an inner function enjoys continues even after the parent functions have returned.
–-This is called closure.
§function getClosure () {
§ var num = 1;
§ var getAlert = function() { num++; alert(num); }
§ num++;
§ return getAlert();
§}
§<input type="button" value="getClosure" onclick="getClosure();">
–function fade(id) {
– var dom = document.getElementById(id),
– level = 1;
– function step () {
– var h = level.toString(16);
– dom.style.backgroundColor =
– '#FFFF' + h + h;
– if (level < 15) {
– level += 1;
– setTimeout(step, 100);
– }
– }
– setTimeout(step, 100);
–}
•JavaScript Namespace
–-Every object is a separate namespace.
–-Use an object to organize your variables and functions.
§var YAHOO = {};
§YAHOO.url = "http://www.yahoo.com";
§YAHOO.getUrl = function () {
§ alert(this.url);
§ return this.url;
§}
§<input type="button" value="YAHOO.getUrl();" onclick="YAHOO.getUrl();">
•Inheritance
–-Linkage provides simple inheritance.
–-Prototypal inheritance.
–-Parasitic inheritance.
–-Method apply(), call().
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 16:30
•Events
•Try…Catch
–try {
–} catch (err) {
–// err.name, err.message
–// err.number, err.description
–}
•Throw
–try {
– throw "error1";
–} catch (err) {
– if ( err == "error1" ) {
– alert("error1 발생");
– }
–}
JavaScript Special Text
|
Code |
Outputs |
|
\' |
single quote |
|
\" |
double quote |
|
\& |
ampersand |
|
\\ |
backslash |
|
\n |
new line |
|
\r |
carriage return |
|
\t |
tab |
|
\b |
backspace |
|
\f |
form feed |
ITWeb/개발일반 2008. 2. 20. 16:28
•JavaScript Loops
–for
§for (var=startvalue;var<=endvalue;var=var+increment) {
§ code to be executed
§}
§for (variable in object) {
§ code to be executed
§}
–while
§while (var<=endvalue) {
§ code to be executed
§}
§do {
§ code to be executed
§} while (var<=endvalue);
–break / continue (break label / continue label)
§for (i=0;i<=10;i++) {
§ if (i==3) {
§ break;
§ }
§ document.write("The number is " + I + "<br />");
§}
§forLable : for (i=0;i<=10;i++) {
§ if (i==3) {
§ continue forLable;
§ }
§ document.write("The number is " + I + "<br />");
§}
–
–with
§with ( document ) { // 반복 시킬 객체
§ write(“생략된 객체 반복1<br>”); // 구문
§ write(“생략된 객체 반복2<br>”); // 구문
§}
|




