20080404 - 로또..
Legacy 2008. 4. 4. 14:36제발 5등이라도 한번만 되어라..ㅡㅡ^

SW 엔지니어 노임 단가ITWeb/스크랩 2008. 3. 31. 16:45이런게 있내요.
지난번 네이버와 다음을 비교 했던 내용과는 사뭇 다르지만.. 개발자 스스로 나는 어디쯤 와 있는지 확인해 볼 필요도 있겠내요.. 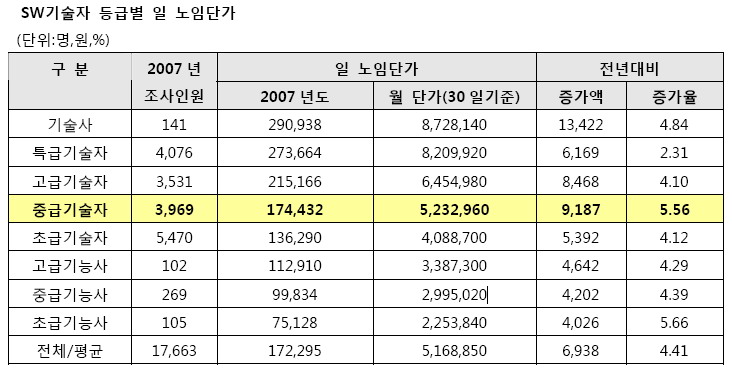 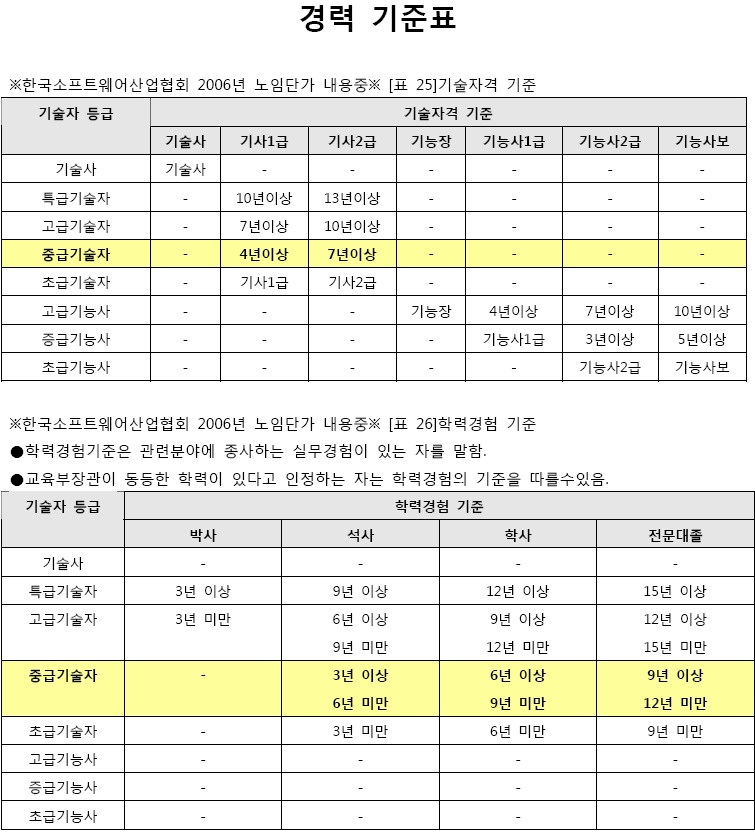 기술자격 기준에 의한 고급기술자 (기사 1급 보유) 학력 기준에 의한 중급기술자 (아직 만 9년이 안되어서.. ) 근데 노임으로 보면.. 저는 정말 좌절 이군요.. 이거 회사에 따져야 하나.. 된장.. 일은 빡시게 하는데.. pay 는 왜 이래.. - 실력이 없거나 인정을 못받고 있거나 ㅡㅜ^ 20080329 - 한강 유람선 타기 실패 그 후 ~Legacy 2008. 3. 31. 12:513/29일 오후 4시 한강 유람선을 타기 위해 곤지암 집에서 출발..
언제나 그렇지만.. 나 에게는 아주 몹쓸 능력이 있습니다. 항상 줄을 서면 그 줄은 이상하게도 줄 생각도 없고 시간도 무지 오래 걸립니다. 역시나 고속도로 톨게이트에서도 줄을 서면 어찌나 앞차에서 문제가 발생을 하는지 남들은 다 빠져 나갔는데 저는 아직도 그러고 있는게 한두번이 아닙니다..ㅡㅡ^ 그런고로 이 날은 고속도록 상황을 파악하기 위해서 전화도 해보았으나 역시.. 나의 선택은 어김 없이 빗나가 줬습니다..ㅡㅡ^ 곤지암 IC 로 진입을 하자 마자.. 어찌나 차가 막히던지..ㅡㅡ^ 겨우 겨우 잠실에 도착 그러나 가지고 있던 입장 티켓이 주말권 두장 평일권 두장..ㅡㅜ^ 뭐.. 이런 저런 이유로 인해서 우리 4월 주말에 유람선을 타자고 다시 합의를 봤습니다..  그 이후 ~~~ 담날 해물탕을 끊여 먹기 위해서 현대백화점에서 해물탕을 하나 샀습니다. 제가 먹어본 완성본 해물탕 중에서는 제일 맛있었던것 같내요.. ^^* 백화점 거의 폐장 시간에 가시면 좀 싸게 구입 하 실수 있습니다. 3~4인용이 9천원 ^^* (아쉬운건 해물탕 사진을 못찍었다는 거..ㅡㅡ^) - 오이, 딸기, 슈.. 백화점에서 장을 마치고 남는 시간에.. 우리는 영화를 보았지요.. "천일의 스캔들" 그냥 골든에이지 보다는 재밌다.. ^^* 이쁜 언니들 둘이 나오죠.. 스칼렛 요한슨, 나탈리 포트만 암튼..  영화를 보고 나서는 역시 시간이 남은 지라.. ㅎㅎ 노래방으로 돌격..  그리고 집으로 돌아 왔답니다.. ^^* 요건 뭐냐구요.. ㅎㅎ 일요일 저녁에.. 곤지암 아이다스 매장가서 나의 운동화를 두켤레 사고 나서 집에서 쫄면 해 먹은 거랍니다..
컵에 담긴건 뭘까요???? 막걸리랍니다.. ^^* 간만에 막걸리를 먹었더니... 맛있더라구요.. ㅎㅎ 암튼.. 나름 유익한 한 주였내요.. :) 잠실 한강 유람선 타러 갈겁니다.. ㅎㅎLegacy 2008. 3. 28. 15:32내일 한강에 유람선 타러 갈겁니다.. ㅋ
그래서 퍼왔습니다..
[펌] cloud computingITWeb/스크랩 2008. 3. 28. 11:15ref. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
Cloud computingFrom Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaCloud computing is a new (circa late 2007) label for the subset of grid computing that includes utility computing and other approaches to the use of shared computing resources. Cloud computing is an alternative to having local servers or personal devices handling users' applications. In general, the label suggests that function comes from "the cloud" -- often understood to mean a public network, usually assumed to be the Internet -- rather than from a specific identifiable device. The label of "cloud computing" is not, however, identical with the business model of software as a service or the usage model of utility computing. Grid computing is a technology approach to manage a cloud. In effect, all clouds are managed by a grid but not all grids manage cloud. Specifically a computer grid and a cloud are synonymous while a data grid and a cloud can be different. Within the general label, though, it is an easy error to assume that all clouds are created equal. This can lead to confusion and disappointment. For example, virtualization of servers on a shared super-server can speed the deployment of new capability, since no new hardware needs to be installed, but the software stack that runs on the virtual server must still be configured and updated -- unlike the case with a multi-tenant software-as-a-service capability. A computer cluster can offer cost-effective service in specific applications, but may be limited to a single type of computing node that allows all nodes to run a common operating system. Alternatively, the canonical definition of grid is one that allows any type of processing engine to enter or leave the system, dynamically, by analogy to an electrical power grid on which any given generating plant might be active or inactive at any given time. However, an electrical generator only needs to produce volts and amperes in synchrony with other units on the grid, while computing cycles are not nearly such an undifferentiated commodity. For example, a computing grid could include both general-purpose processors and specialized units such as a vector processor facility. Also important to the notion of cloud computing is the automation of many management tasks. If the system requires human management to allocate processes to resources, it's not a cloud: it's just a data center. The applications of cloud/utility computing models are expanding rapidly as connectivity costs fall, and as evolution of processor architectures favors the development of multi-core systems with intrinsically parallel computing hardware that greatly exceeds the parallelization potential of most applications. The economic incentives to share hardware among multiple users are increasing; the drawbacks in performance and interactive response that used to discourage remote and distributed computing solutions are being greatly reduced. As a result, the services that can be delivered from the cloud are not limited to web applications, but may also include storage, raw computing, or access to any number of specialized services. Common visualizations of a cloud computing approach include, but should not be considered to be limited by, the following:
[edit] Potential advantagesPotential advantages of any cloud or grid computing approach include:
[edit] EnsemblesWhile most traditional IT clouds are made up of heterogeneous systems, an ensemble is a pool of homogenous systems within the cloud which are compatible with one another. These ensembles are integrated by virtualization and management software which allow for mobility of the software stack between physical servers. It can scale from a few servers to many thousands, while having the management complexity near that of a single system. For instance an ensemble could be a set of systems which are capable of running a certain web appliance stack. The operating system, middleware, and web-app run exactly the same between servers in the ensemble. [edit] ArchitectureThe architecture behind cloud computing is a massive network of "cloud servers" interconnected as if in a grid running in parallel, sometimes using the technique of virtualization to maximize computing power per server. A front-end interface allows a user to select a service from a catalog. This request gets passed to the system management which finds the correct resources, and then calls the provisioning services which carves out resources in the cloud. The provisioning service may deploy the requested stack or web application as well.
[edit] Cloud storageCloud storage is a model of networked data storage where data is stored on multiple virtual servers, generally hosted by third parties, rather than being hosted on dedicated servers. Hosting companies operate large data centers; and people who require their data to be hosted buy or lease storage capacity from them and use it for their storage needs. The data center operators, in the background, virtualize the resources according to the requirements of the customer and expose them as virtual servers, which the customers can themselves manage. Physically, the resource may span across multiple servers. [edit] Cloud servicesCloud services refers to web services offered via cloud computing. Amazon is probably the first company to start selling Cloud based services in the form of its Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud, popularly known as Amazon EC2, a part of Amazon's web services platform. Currently in its beta version, it provides computing capacity in the cloud to run applications |